¶ RP-Lidar 360°
Lidar 2D
Evolutions possibles:
- Etablir une connexion WiFi entre le Lidar et le PC processing 3
- ajouter une mécanique perméttant d'intégrer le troisième axe et avoir une rprésentation 3D de l'espace
 |
 |
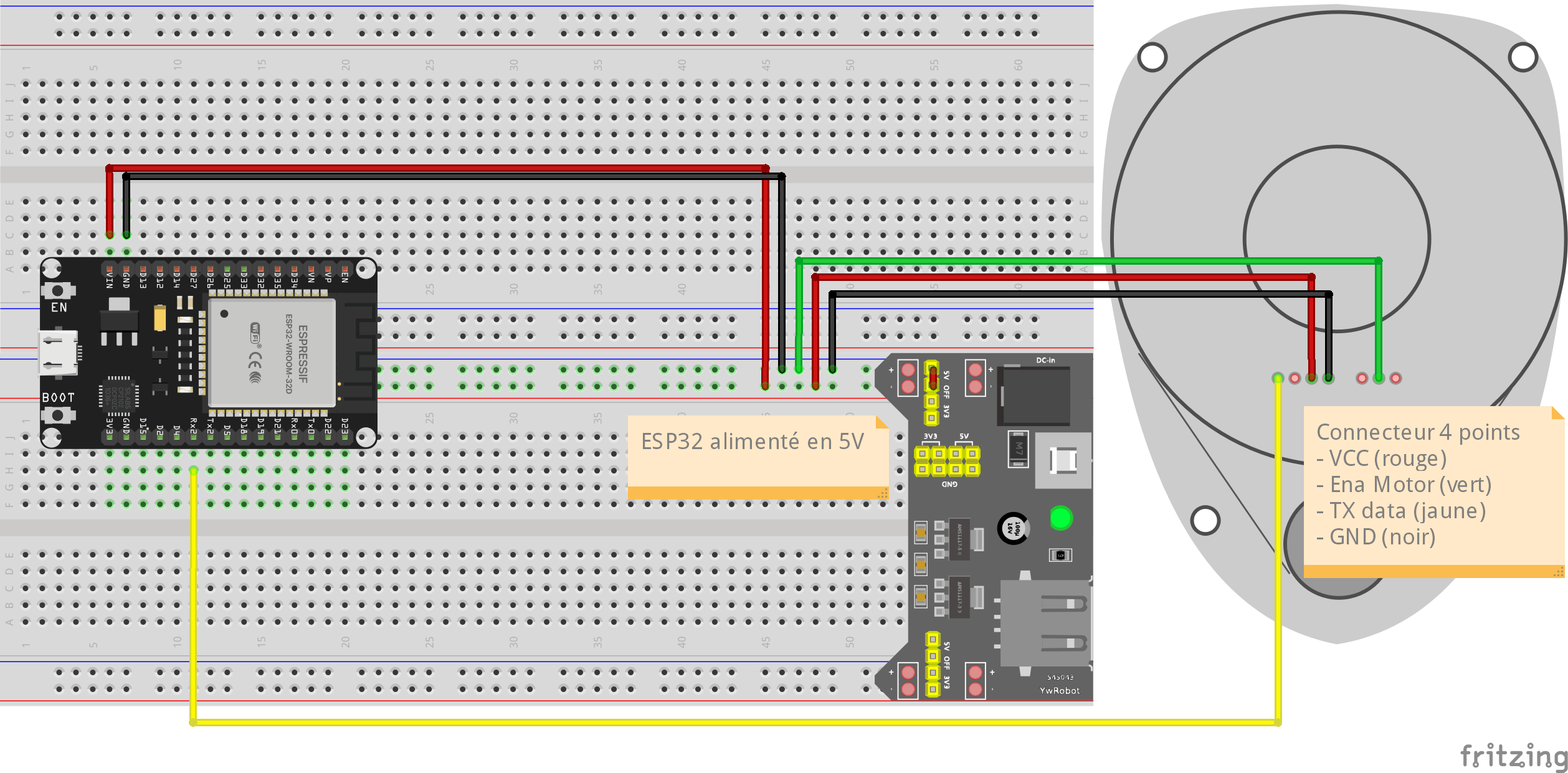
¶ Rôles des 4 fils
| Couleur | Fonction | Direction | Commentaire |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rouge | +5 V | — | Alim moteur + électronique |
| Noir | GND | — | Masse |
| Jaune | TX du LiDAR → micro | Sortie | Données série (230400 bauds) |
| Vert | MOTOR_EN / ENABLE | Entrée | Active la rotation (HIGH = ON) |
¶ Arduino
/******************************************************************
* LiDAR X-WPFTB-V2.x - ESP32 WROOM
* Envoi des points en XY sur le port USB :
* "P x y\n" (x,y en cm, entiers)
******************************************************************/
static const int LIDAR_RX = 16; // LiDAR TX -> ESP32 RX2
static const int LIDAR_TX = 17; // (pas utilisé)
static const int LIDAR_EN = 4; // fil vert ENABLE moteur
static const int FRAME_SIZE = 60;
uint8_t frameBuf[FRAME_SIZE];
int frameIndex = 0;
bool synced = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // <-- COM20 à 115200 dans Processing
delay(1000);
Serial.println("=== LiDAR X-WPFTB - ESP32 ===");
pinMode(LIDAR_EN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LIDAR_EN, HIGH);
Serial2.begin(230400, SERIAL_8N1, LIDAR_RX, LIDAR_TX);
}
// ---------- Décodage & envoi XY ----------
void decodeFrame(uint8_t* buf) {
uint8_t type = buf[2];
uint8_t dataLen = buf[3];
if (type != 0x07 || dataLen != 0x0C) {
return; // on n'utilise que les trames de mesures
}
uint16_t startRaw = buf[6] | (uint16_t(buf[7] & 0x7F) << 8);
int16_t startCode = int16_t(startRaw) - 0x2000;
float startAngleDeg = startCode / 64.0f;
uint16_t endRaw = buf[56] | (uint16_t(buf[57] & 0x7F) << 8);
int16_t endCode = int16_t(endRaw) - 0x2000;
float endAngleDeg = endCode / 64.0f;
const int N = 12; // 12 points
float delta = endAngleDeg - startAngleDeg;
if (delta < -180.0f) delta += 360.0f;
if (delta > 180.0f) delta -= 360.0f;
float step = (N > 1) ? (delta / (N - 1)) : 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int base = 8 + i * 4;
uint8_t dL = buf[base + 0];
uint8_t dH = buf[base + 1];
uint16_t distCode = (uint16_t(dH) << 8) | dL;
float dist_mm = distCode * 0.1f;
float angleDeg = startAngleDeg + i * step;
if (angleDeg < 0) angleDeg += 360.0f;
if (angleDeg >= 360.0f) angleDeg -= 360.0f;
// On envoie "D angle distance"
Serial.print("D ");
Serial.print(angleDeg, 2);
Serial.print(' ');
Serial.println(dist_mm, 1);
}
}
// ---------- Boucle de synchro ----------
void loop() {
while (Serial2.available()) {
uint8_t b = Serial2.read();
if (!synced) {
if (frameIndex == 0) {
if (b == 0x55) {
frameBuf[frameIndex++] = b;
}
} else if (frameIndex == 1) {
if (b == 0xAA) {
frameBuf[frameIndex++] = b;
synced = true;
} else {
frameIndex = 0;
}
}
continue;
}
frameBuf[frameIndex++] = b;
if (frameIndex == FRAME_SIZE) {
decodeFrame(frameBuf);
frameIndex = 0;
synced = false;
}
}
}
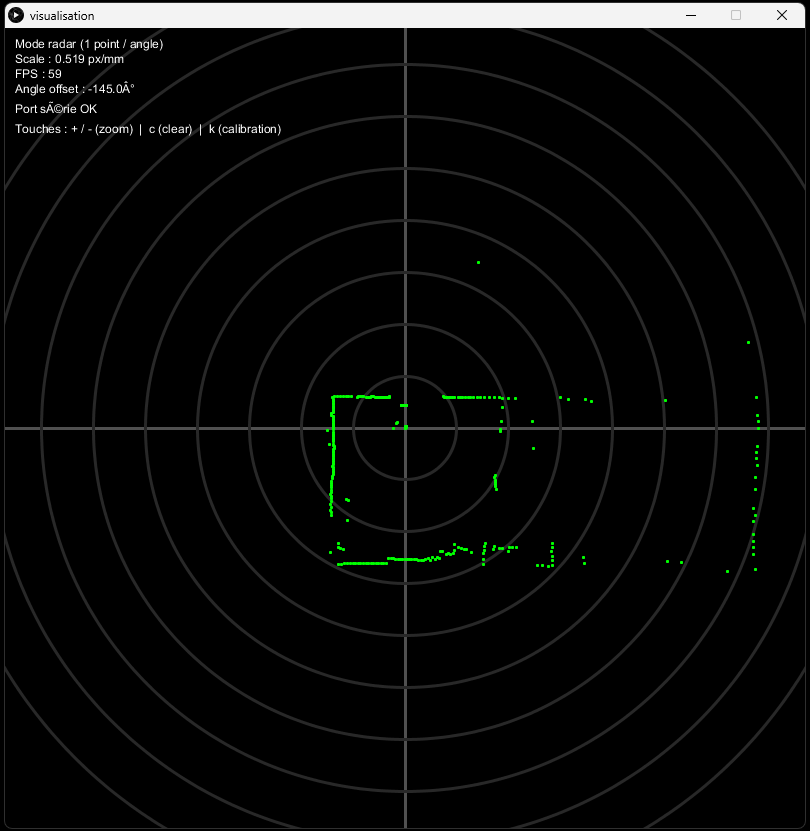
¶ Processing
add_library('serial')
from processing.serial import Serial
import math
# --- Paramètres ---
# distance par angle (0..359), en mm
dist_by_angle = [0.0] * 360
scale = 0.2 # pixels par mm
ANGLE_OFFSET = -145.0 # offset initial (à ajuster)
lidarPort = None
buffer = "" # buffer de réception série
def setup():
global lidarPort
size(800, 800)
background(0)
frameRate(60)
ports = Serial.list()
print("Ports disponibles :", ports)
# chez toi, COM20 est à l'index 1
if len(ports) > 1:
portName = ports[1]
print("Ouverture du port :", portName)
try:
lidarPort = Serial(this, portName, 115200)
# on lit manuellement dans draw()
except Exception as e:
print("Erreur à l'ouverture du port série :", e)
lidarPort = None
else:
print("Pas assez de ports détectés.")
lidarPort = None
def draw():
global buffer
# 1) Lecture du port série
if lidarPort is not None:
while lidarPort.available() > 0:
c = chr(lidarPort.read())
buffer += c
if c == '\n':
msg = buffer.strip()
buffer = ""
# debug si besoin :
# print("RAW:", repr(msg))
handleMessage(msg)
# 2) Affichage radar
background(0)
translate(width/2, height/2)
# axes
stroke(80)
line(-width/2, 0, width/2, 0)
line(0, -height/2, 0, height/2)
# cercles 1m / 2m / 3m
noFill()
stroke(40)
for d in range(10):
ellipse(0, 0, 2*d*100*scale, 2*d*100*scale)
# points : 1 par angle
stroke(0, 255, 0)
strokeWeight(3)
for ang in range(360):
d = dist_by_angle[ang]
if d <= 0:
continue
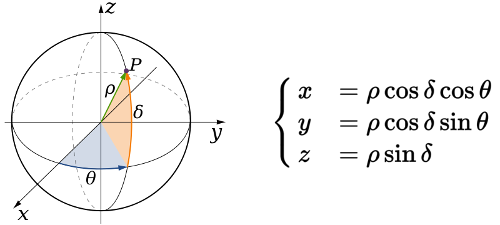
a_rad = math.radians(ang)
x = -d * math.cos(a_rad) * scale
y = -d * math.sin(a_rad) * scale
point(x, y)
# overlay texte
resetMatrix()
fill(255)
text("Mode radar (1 point / angle)", 10, 20)
text("Scale : %.3f px/mm" % scale, 10, 35)
text("FPS : %d" % frameRate, 10, 50)
text("Angle offset : %.1f°" % ANGLE_OFFSET, 10, 65)
if lidarPort is None:
text("Port série NON ouvert", 10, 85)
else:
text("Port série OK", 10, 85)
text("Touches : + / - (zoom) | c (clear) | k (calibration)", 10, 105)
def handleMessage(msg):
global dist_by_angle, ANGLE_OFFSET
if not msg:
return
# on attend "D angle distance"
if not msg.startswith('D'):
# autres messages éventuels
# print("DBG:", msg)
return
parts = msg.replace(',', ' ').split()
if len(parts) < 3:
# print("DBG (format invalide):", msg)
return
try:
angle_deg = float(parts[1])
dist_mm = float(parts[2])
# filtrage simple : ignore distances nulles ou ridicules
if dist_mm < 1:
return
# applique l'offset d'angle
angle_corr = (angle_deg + ANGLE_OFFSET) % 360.0
# arrondi à l'angle entier le plus proche
idx = int(round(angle_corr)) % 360
dist_by_angle[idx] = dist_mm
except Exception as e:
print("Parse error:", msg, "->", e)
def calibrate():
"""Calibre ANGLE_OFFSET en prenant le point le plus proche comme 'devant'."""
global ANGLE_OFFSET, dist_by_angle
minDist = 1e9
bestAng = 0
for ang in range(360):
d = dist_by_angle[ang]
# on ignore les distances trop faibles ou nulles (bruit)
if d > 50 and d < minDist:
minDist = d
bestAng = ang
ANGLE_OFFSET = -float(bestAng)
print("Calibration OK -> ANGLE_OFFSET =", ANGLE_OFFSET, " (minDist =", minDist, "mm)")
def keyPressed():
global scale, dist_by_angle
if key in ['c', 'C']:
dist_by_angle = [0.0] * 360
elif key == '+':
scale *= 1.1
elif key == '-':
scale /= 1.1
elif key in ['k', 'K']:
calibrate()